Jawless fish represent one of the most ancient and primitive groups of vertebrates. Unlike most fish, these creatures lack jaws and paired fins, giving them a distinct appearance and set of behaviors. Despite their simple structure, jawless fish have thrived for hundreds of millions of years, adapting to various environments and playing essential roles in marine ecosystems. This article delves into the basics of jawless fish, exploring their unique characteristics, types, and significance.

Jawless Fish
Defining Jawless Fish
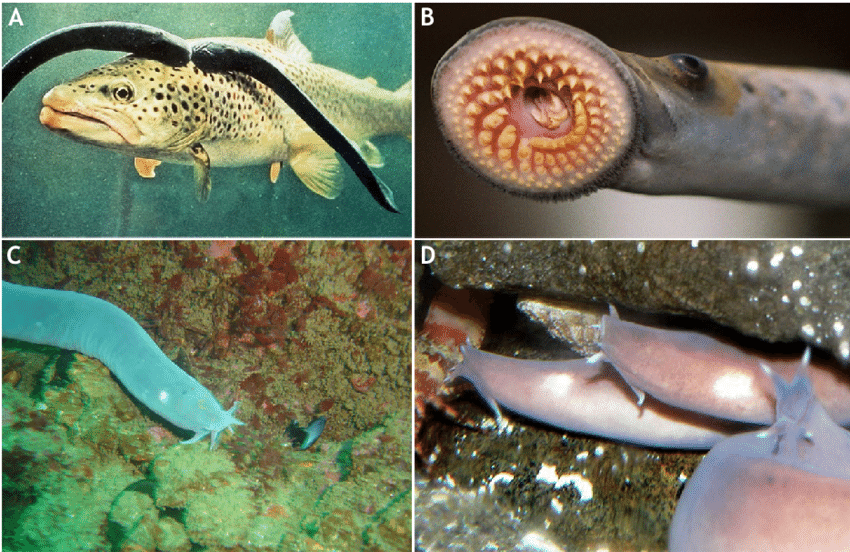
Jawless fish, scientifically known as Agnatha, belong to a superclass that includes only two existing groups: lampreys and hagfish. These fish are characterized by their lack of true jaws, a feature that sets them apart from the vast majority of vertebrates. Instead of jaws, they have circular, sucker-like mouths filled with rows of teeth or tooth-like structures, which they use to latch onto or feed on other animals.
Moreover, jawless fish lack paired fins, a backbone, and scales, which are common features in most other fish species. Their bodies are elongated and eel-like, with soft, flexible skin that often produces copious amounts of slime. Despite their primitive features, jawless fish have successfully adapted to various habitats, from deep ocean floors to freshwater rivers.
The Two Main Types of Jawless Fish
Lampreys
Lampreys are perhaps the most well-known group of jawless fish. They have a parasitic lifestyle, often attaching themselves to other fish with their suction-cup-like mouths. Once attached, lampreys use their sharp teeth to scrape away the host’s skin and feed on its blood and bodily fluids. This parasitic behavior can be harmful to the host fish, leading to significant declines in fish populations in areas where lampreys are invasive.
Furthermore, lampreys are anadromous, meaning they spend part of their lives in the ocean and return to freshwater rivers to spawn. Their life cycle involves a lengthy larval stage, during which they burrow into riverbeds and filter-feed on microscopic organisms. Hence, lampreys play a dual role in the ecosystem: as parasites and as filter feeders during their larval stage.
Hagfish
Hagfish, often referred to as “slime eels,” are another group of jawless fish known for their unique defense mechanism. When threatened, hagfish can produce large quantities of slime, which can clog the gills of predators or allow them to slip away. This slime is so effective that it has garnered interest from scientists and engineers for potential applications.
In addition to their slime production, hagfish have a scavenging lifestyle, feeding primarily on dead or dying animals. They use their tooth-like structures to rasp away flesh, often burrowing into the carcasses of larger animals to consume them from the inside out. Therefore, hagfish play a crucial role in the marine ecosystem by breaking down and recycling nutrients from dead organisms.
The Evolutionary Significance of Jawless Fish
Jawless fish hold a significant place in the evolutionary history of vertebrates. They are among the earliest vertebrates, with fossil records dating back over 500 million years to the Cambrian period. The lack of jaws in these fish represents a primitive stage in vertebrate evolution, preceding the development of more complex structures like jaws and paired fins.
Furthermore, the study of jawless fish provides valuable insights into the evolution of vertebrates. By examining the biology and genetics of lampreys and hagfish, scientists can better understand how early vertebrates evolved and adapted to their environments. Thus, jawless fish are not only fascinating in their own right but also essential to understanding the broader evolutionary history of life on Earth.
The Ecological Role of Jawless Fish
Despite their primitive appearance, jawless fish play vital roles in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Lampreys, as parasites, help control fish populations and maintain ecological balance. In areas where they are invasive, however, they can cause significant ecological and economic damage, highlighting the complexity of their role in the ecosystem.
Hagfish, on the other hand, are important scavengers, cleaning up dead and decaying matter from the ocean floor. By consuming carrion, they recycle nutrients and help maintain the health of the marine environment. Additionally, their slime production contributes to the unique dynamics of predator-prey interactions in the ocean.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Jawless fish, with their unique characteristics and ancient lineage, offer a glimpse into the early stages of vertebrate evolution. Lampreys and hagfish, the two main types of jawless fish, have adapted to diverse environments and play important roles in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Moreover, their evolutionary significance and ecological contributions make them a fascinating subject of study for scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. As we continue to explore the depths of our oceans and rivers, jawless fish remind us of the incredible diversity and adaptability of life on Earth.